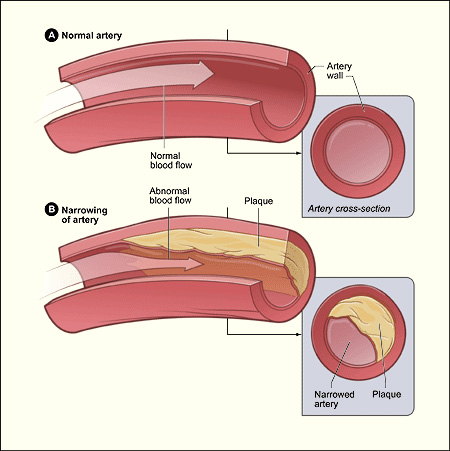
A heart attack or myocardial infarction occurs when oxygenated blood does not get to part of the heart due to a blockage or occlusion in one or more of the coronary arteries. Without blood and oxygen, part of the heart muscle dies.
Heart Attack or Myocardial Infarction
A heart attack does not feel the same for every person.
The most common sign of a heart attack is a feeling of pressure or heaviness on your chest, or chest tightness. Pain may extend to the neck, jaw, shoulders, or down the arm. Lightheadedness, fainting, sweating, nausea or shortness of breath may accompany pain. Other signs may include an uncomfortable pressure, fullness, tightness, or burning sensation under the breastbone. These symptoms are referred to as "atypical chest pain" and initially may not be recognized as a symptom of a heart attack. Women frequently have less common signs of a heart attack such as atypical chest pain, stomach or abdominal pain, nausea or dizziness, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing, unexplained anxiety, weakness, fatigue, or palpitations.
If you are a person with no history of heart disease, and you get any of the above symptoms you should do the following:
- Stop activity and sit or lie down
- Call 911 if pain continues for more than 5 minutes
If you have heart disease and develop any symptoms, you should:
- Stop activity and sit or lie down
- Take nitroglycerin under your tongue - one tablet every five minutes for a maximum of three tablets until the symptoms are gone
- Call 911 if the symptoms continue
Call 911! DO NOT DRIVE YOURSELF OR ALLOW ANYONE ELSE TO DRIVE YOU TO THE HOSPITAL!
Treatment begins as soon as the emergency personnel arrive. This can make a difference since early treatment of a heart problem improves your chances of a successful outcome.