
Whether it's paleo, high-protein keto, Atkins or something else — high protein diets have been a trending topic for decades and remain relevant today. Just take a look at social media where #HighProteinMeals currently has billions of views, and you'll find thousands of posts from people speaking about their diets and showcasing their protein-rich recipes.
So, what is protein and how much of it should you consume daily? Finding the right balance of protein is key. Whether you're an athlete, fitness enthusiast or simply looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle, the question of how much protein is too much is an important one to ask yourself.
What is the Role of Protein?
"Protein is a macronutrient, one of three essential macronutrients your body needs to function along with carbohydrates and fats," says Maureen Boccella, MS, RD, CDCES, LDN, Manager, Nutrition and Diabetes Services, Chester County Hospital. "It's made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of your body. These amino acids help in the development of muscles, organs, and tissues, supporting growth and repair throughout your body."
Protein plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, making them a key factor in ensuring your body is working properly every day. Some foods that are rich in healthy proteins include fish and shellfish, beans, nuts, peanuts, soybeans and more.
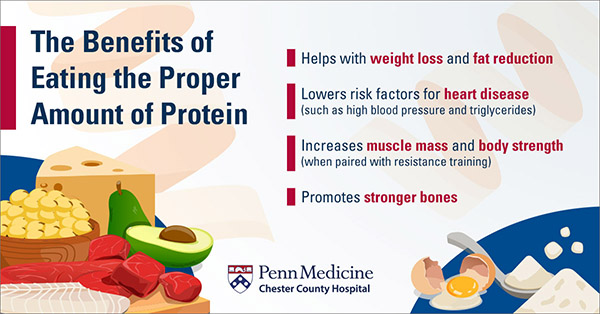
Protein is also essential for maintaining a healthy immune system, as it helps produce antibodies that defend against infections and illnesses. Additionally, protein contributes to a feeling of fullness, helping with weight management by reducing overeating.
The Risks of Too Much Protein
While protein is undoubtedly beneficial, as the old adage goes — too much of anything can always have a negative impact. Consuming too much protein can lead to various health risks, including:
- Nutrient Imbalances: A diet overly focused on protein might neglect other essential nutrients like carbohydrates and fats. Carbohydrates, for example, are crucial for providing a faster energy source to the body, especially during physical activities. If you're overloading on protein, you may be neglecting your carb intake, leading to less energy and fewer benefits.
On the other hand, a well-rounded diet that includes a balance of proteins, carbohydrates and fats can be beneficial — and striking the right mix can lead to better health overall.
- Digestive Issues: High protein intake can lead to constipation, bloating and discomfort. This is because protein-rich foods often lack the fiber found in foods like fruits, vegetables and whole grains, which are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
While you load up on your lean meats, seafood and dairy, make sure you're also adding some fruits and veggies to the mix for optimal digestion. Incorporate salads, broccoli, spinach or other options to your dinner. Add a smoothie to your breakfast and opt for fruits as a snack throughout the day to help you find a healthy balance.
- Potential Adverse Effects On Your Mental Health: Scientists are researching if low-carb diets like keto might also impact mental health. Some researchers also have a theory that carbs are responsible for releasing serotonin, which boosts your mood, so eating a moderate amount of carbs may reduce the risk of anxiety and depression. Incorporate complex carbs like legumes, fruits, starchy vegetables and whole grains into your diet along with healthy proteins.
- Kidney Damage and Frequent Urination: Excessive protein intake can even affect your kidney health. The kidneys play an important role in filtering waste products from your blood. However, too much protein can put strain on these organs and how they function. Individuals with preexisting kidney conditions may be more prone to complications.
Additionally, researchers have found that people who incorporated plant-based and low-fat dairy to protein diets had a lower risk of developing kidney stones than those who ate animal-based foods like meat and had low calcium diets.
Another study found that people who consumed more protein in the evening tended to expel higher amounts of urea, a compound that is released in urine, during the night. The study suggested that, apart from water and salt, urea plays a significant role in the production of urine and concluded that reducing protein intake in the evening could be a helpful lifestyle change for managing frequent urination at night related to higher protein consumption.
- Heart Problems: Too much protein can even lead to heart problems. Some high-protein diets, particularly those rich in red and processed meats, have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular issues. Choose lean protein sources while incorporating a variety of foods into your diet and explore delicious and healthy recipes to maintain heart health.
Implementing a Balanced Diet for Optimal Nutrition
Boccella says it's important to prioritize a balanced diet that includes a mix of protein sources -- such as lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, legumes, nuts and seeds -- which provide the necessary amino acids your body needs without excessive protein intake. "Plant-based protein sources, such as beans and lentils, also offer additional benefits, including fiber and essential vitamins."
While the risks of too much protein are evident, it's crucial to strike a balance and ensure you’re incorporating the proper amount into your diet. How much protein you should eat depends on your age, sex, and activity level. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine your specific protein needs so you can maintain optimal health.
Interested in Maximizing Your Nutritional Intake?